Gemstone Buying Guide
Gemstone Certificate Report: How to Read & Actually understand It

Before diving into the details about how to read a gemstone certificate report, you need to first understand what is a gemstone certificate report and why it is so important.
We, at Rajendra’s Gems, deal in only government certified gemstones to ensure the stone’s authenticity and be a trusted source for all our clients. Most of the stones are certified by GJEPC, India, the best government lab in India with the most high-end range of equipment.
What is a gemstone certificate report?
A gemstone certificate is required to ascertain the quality of a gemstone. It is essentially a blueprint of the gemstone detailing all the key elements of the stone. Basis the attributes of the gemstone in the report, it becomes easier to decide the authenticity of a stone. Since you are investing a hefty sum in buying gemstones online or from a shop near you (irrespective of the type), a gemstone certificate report ensures you are buying a genuine product.
The vital points covered in the report may vary depending on the different gemological testing lab reports you are viewing. Trained gemologists examine your stone and based on the mix of scientific analysis and expert inspection draft a report which is helpful in finding the nature and authenticity of the gem. A typical gemstone certificate report would have a picture of the gem on one side with its details mentioned on the other.

Common elements in a gemstone certificate report
The basic details highlighted in a gemstone certification report are its quality of gems (natural or synthetic), carat weight, shape & cut, colour, measurement of the stone, optic character, specific gravity, refractive index & hardness and species. The comments mentioned in the report also carry a high importance in these tests. The attributes of each report differ compared to the technologies they are using and the scientific approach they are considering. However, the features mentioned above are more or less present in every gemstone testing report.
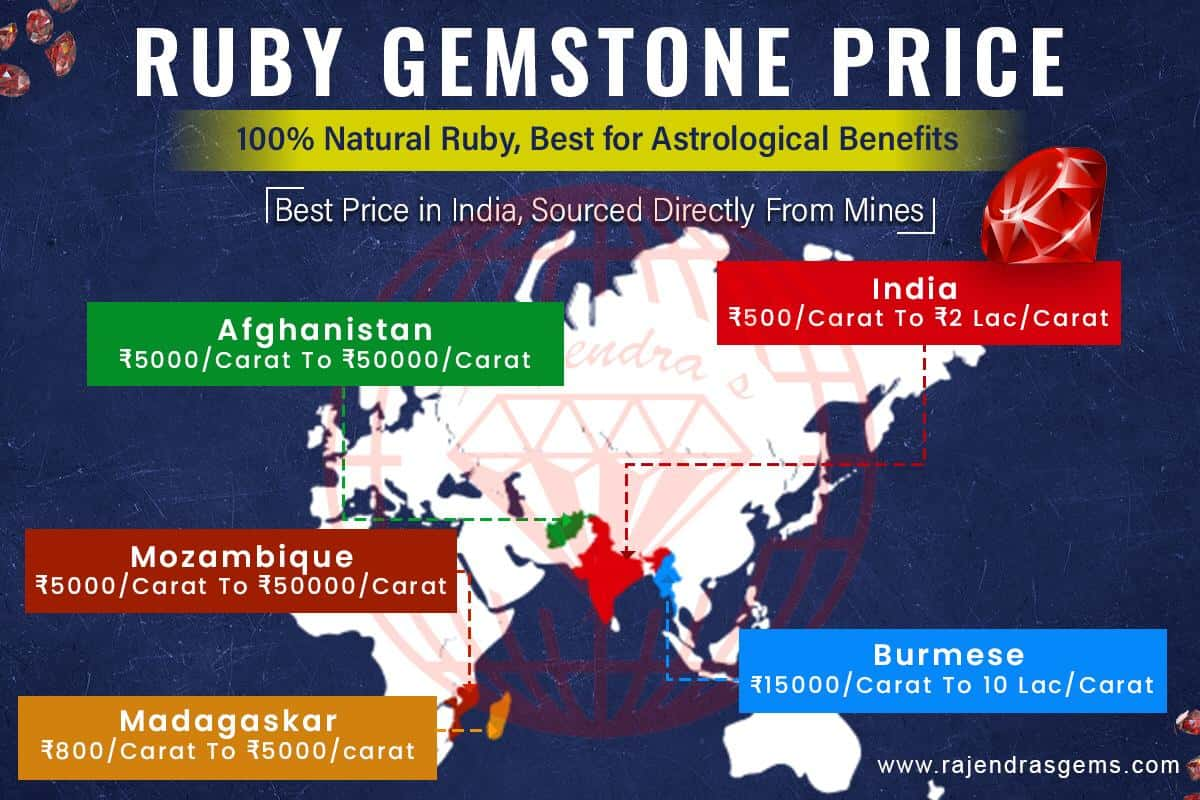
Let’s take an example of the most trusted gemstone certification lab in India – IGI-GTL – GJEPC – and understand how it presents its report.
A typical gemstone report from government recognised Indian Gemological Institute – Gemological Testing Laboratory (IGI-GTL) will have following elements:
1. Report No.
On the top left, you’ll find the stone report number which may be used whenever you need a duplicate copy of the report from the lab.
2. Date
On the top right, you’ll find the date of the testing. The tests done after April 1, 2019 are uploaded online. So, if you wish to check any particular report, you can go to their website and view the report through the report number.
3. Type of stone
The title lists the type of stone, which could be Sapphire, Emerald, Ruby or others.
4. Colour
This section lists the colour of the gemstone. Colour is a very important factor when it comes to use of gemstone particularly for astrological benefits.
5. Weight
The total weight of the gemstone is mentioned here in carats.
6. Description
In this section, it will mention whether the gemstone is mounted or unmounted. If it is integrated in a ring, it will be termed as mounted. In general, the gemstones are certified in its original condition and then mounted in a ring or any other jewellery.
7. Shape & Cut
Under shape & cut, the structure of the gemstone will be summarised as oval, round or mix.
8. Dimensions
The size of the gemstone is mentioned under dimensions. No two untreated stones are of the same size; hence, you can verify the stone through this attribute as well.
9. Transparency
This pointer lets you know whether the gemstone is transparent or opaque.
10. Other Test
There are different technical tests used to determine specific characteristics of the gemstone to ascertain its authenticity. Tests conducted such as IR spectra analysis, microscopic observation or others are mentioned in this section.
11. Comments
The last section mentions whether the stone is subjected to heat or treated with a particular chemical to change its outer appearance or there are any kinds of fracture filling done, etc.
12. Seal of trust and authenticity
Lastly, the report is signed and verified by the authorized signatory of IGI- GTL.
Which are the prominent Gemstone certification labs?
There are various gemstone certification labs available in India, which conduct tests to ascertain the authenticity of the gemstone. However, there are chances of lack of authoritativeness and high-end equipment in many of these non-popular gemstone labs, hence, if you are purchasing a gemstone ensure that it is certified by prominent gemstone testing labs of the country. Some of the popular ones include Indian Gemological Institute, (IGI-GTL GJEPC), Gemological Institute of America (GIA), Gemological Laboratory Of India (GLI), Gübelin Gem Lab .
How much does lab certification costs for a gemstone?
The cost of certification in India from a reputed lab is about Rs. 1500, on average and usually ranges from Rs. 600 to Rs. 2000.
Is the cost worth it?
For premium stones with higher value, we suggest going for the most trusted IGI-GTL GJEPC. For other gemstones, preferably under Rs. 15000, we would suggest you can opt for a more economical and cheaper alternative for low-cost products.
Why does the report format vary from lab to lab?
The prime reason for the format difference is the availability of different types of equipment present at the respective gemstone testing lab. Some labs have advanced machinery for testing and look for in-depth analysis of each gemstone. The report from such labs may be a little costly but the report is more authentic compared to the local gem testing labs.
How to read abbreviations in a Gemstone Certificate Report?
There are some key abbreviations you need to know for understanding a gemstone certificate report. These abbreviations are used across a few gemstone testing reports. Here you go.
- B: Indicates the gemstone has been bleached or lightened.
- C: The gemstone has been coated with a substance to alter its appearance or achieve a desired effect.
- E: Enhanced gemstone using commonly accepted treatments (for example, heat-treating for sapphire and rubies or oiling for emeralds).
- G: Irradiated gemstone by gamma or electron bombardment.
- H: The gemstone has been heat treated.
- I: A non-traditional enhancement was used (such as flux or lead glass filling in rubies).
- L: Indicates laser drilling to remove dark inclusions in diamonds.
- N: This testifies that the gemstone is a natural gemstone and not enhanced.
- O: The gemstone has been oiled.
- R: Irradiated gemstone by neutron bombardment.
- S: Indicates a bonding element that has been introduced to give the gemstone durability.
- U: A diffusion treatment was used to alter the appearance of the gemstone.
- W: Wax or oil is used to improve a gemstone’s appearance